The Open RAN (O-RAN) technology has brought about a flexible and innovative network architecture that overcomes the limitations of traditional RANs and promotes an agile industry. However, many service providers hesitate to adopt O-RAN technology due to existing RAN capex and management challenges. This blog highlights the challenges O-RAN adopters face and proposes a real-world approach to achieve optimal network optimization and cost management.
When do we need O-RAN: Now!
Potential risk #1 Incompatibility with current infrastructure
Network operators have long recognized the need for open, dedicated and software-defined networks. Despite efforts to implement and test these networks, CSPs were restricted due to vendor lock-in, resulting in limited success (only a few patches in 4G core networks).
With the Service-Based Architecture (SBA) introduced by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in 5G, the wireless industry has entered a new era of transformative change, paving the way for a seamless transition to next-generation networks. The standardization introduced by 3GPP opened the doors for continuous testing with a wide range of hardware and software implementation scenarios.
Conventional OEMs adapted their product offerings to align with industry trends, allowing multi-vendor RAN deployments and interoperability between multiple components in a Virtual RAN (vRAN).
vRAN decouples hardware from software, giving operators some elbow room to choose any hardware from the market. However, it is yet to fully meet the cost expectations of network operators, as they still need to pay recurring fees for network functions and licenses. Also, it did not pave the way for a truly open network.
O-RAN goes a step further in disaggregating RAN. The open architecture enables customized network solutions tailored to specific requirements, addressing the limitations of traditional RANs and covering the way for a more agile and responsive industry.
Benefits of O-RAN adoption
According to various market research reports, RAN accounts for nearly 60-65 percent of the total cost of network ownership. The dominant position of OEMs made the RAN components of the wireless network more expensive.
However, with the advent of Open RAN, operators can save up to 30 percent in total cost of ownership (TCO) with the right platform strategy and skill set, as per a report by Analysysmason. O-RAN enables CSPs to control the network efficiently and manage expenses by incorporating:
- Open interfaces: Standardized and open interfaces (in line with 3GPP standards) break vendor lock-in, fostering multi-vendor interoperability. Network operators can customize their networks by selecting components from different vendors.
- Service Orchestration: The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) orchestrates multi-vendor RAN components, implementing AI/ML for proactive issue detection and response. It helps manage complexity and gain spectral efficiency, resulting in a self-healing network, minimizing downtime and enhancing reliability.
- Cloud-centric approach: Open RAN runs network functions on standard servers in data centres or the cloud, reducing costs and enhancing scalability and agility.
- Containerized Microservices Architecture: Embracing a microservices approach streamlines the development, deployment, and scaling of telecom applications, fostering efficiency in service delivery.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Seamlessly integrating with CI/CD pipelines, Open RAN automates testing, deployment, and monitoring, ensuring rapid feature delivery without downtime during deployments.
Challenges in the adoption of O-RAN
Open RAN represents an ideological movement rooted in the belief that a diverse ecosystem of radio suppliers promotes innovation through competition, leading to a lower cost of ownership. That said, it could lead to service issues if not integrated appropriately. So, CSPs need to be aware of O-RAN’s impact on:
- Interoperability: The interoperable nature means more complexity, which could lead to increased latency or downtime. Collaboration between different equipment vendors is needed to avoid compatibility issues.
- Security: The disaggregation of O-RAN functions increases the attack surface. Service providers must consider the latency demands before implementing additional security controls.
- Network performance and management: Ensuring consistent performance across different vendors is crucial for user satisfaction. Managing a network with multiple vendors requires advanced tools, expertise and changes to existing frameworks, processes, and governance approaches.
- Vendor adoption: More vendors must adopt O-RAN technology to expand the available options and foster competition.
Despite these challenges, O-RAN has gained significant traction, with industry leaders showing interest and initial testing proving its feasibility.
The coexistence of RAN and O-RAN
O-RAN also provides the standard open interfaces to coexist with existing RAN infrastructure, thereby protecting RAN investments. The coexistence promises a balanced (cost/performance) approach to the evolution of radio access networks. Adhering to standards also determines future success.
This allows for seamless integration, migration, cost-effective upgrades, and customized service levels to meet the diverse needs of retail and enterprise customers.
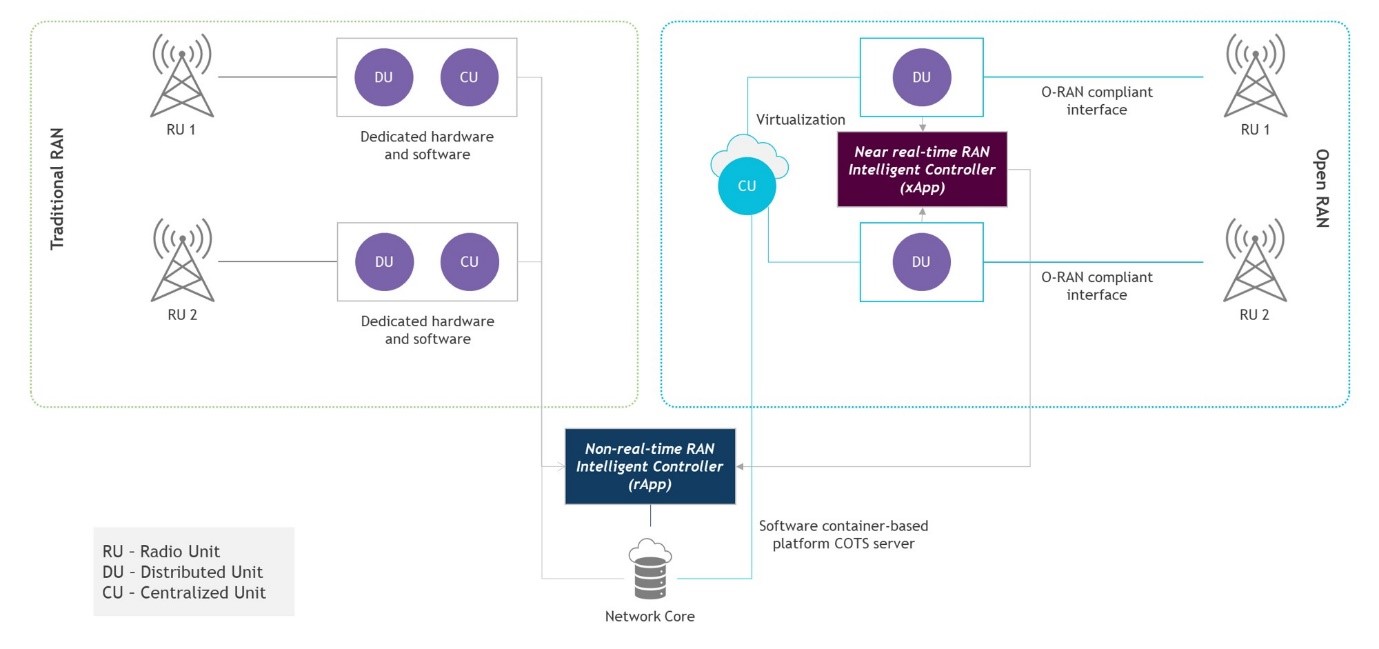
Figure 1 – Coexistence of RAN and O-RAN
Several key trends and developments will shape the future of this coexistence:
- Sustained innovation: As edge computing gains momentum, the convergence of RAN and edge computing will be vital for low-latency applications and services, such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and autonomous vehicles.
- Empowering network slicing: O-RANs software-defined capabilities will enable network slicing, allowing operators to create customized and isolated virtual networks tailored to specific user requirements, applications, and industries.
- Increased security measures: With the expansion of network functionalities, the focus on cybersecurity will intensify. Robust security measures will be crucial to safeguard RAN and O-RAN networks from potential threats.
- The ongoing adoption of 5G, mobile private networks and beyond: The deployment and optimization of 5G networks will remain a primary focus for network operators. The openness and intelligence of O-RAN will play a pivotal role in unlocking the full potential of 5G and paving the way for future technologies.
- Costing and supply chain control: The strategic cost and supply chain control ensures that deploying and maintaining networks remains economically viable and technically ahead.
As these trends impact CSPs, O-RAN is expected to drive innovation, reduce vendor lock-in, reduce feature-based pricing and boost industry cost effectiveness.
What’s the best way to O-RAN?
The best approach to realizing Open RAN from the lab to the live network is balancing performance and openness. An Open RAN architecture presents a significant opportunity for network operators to enhance flexibility, agility, and cost-effectiveness.
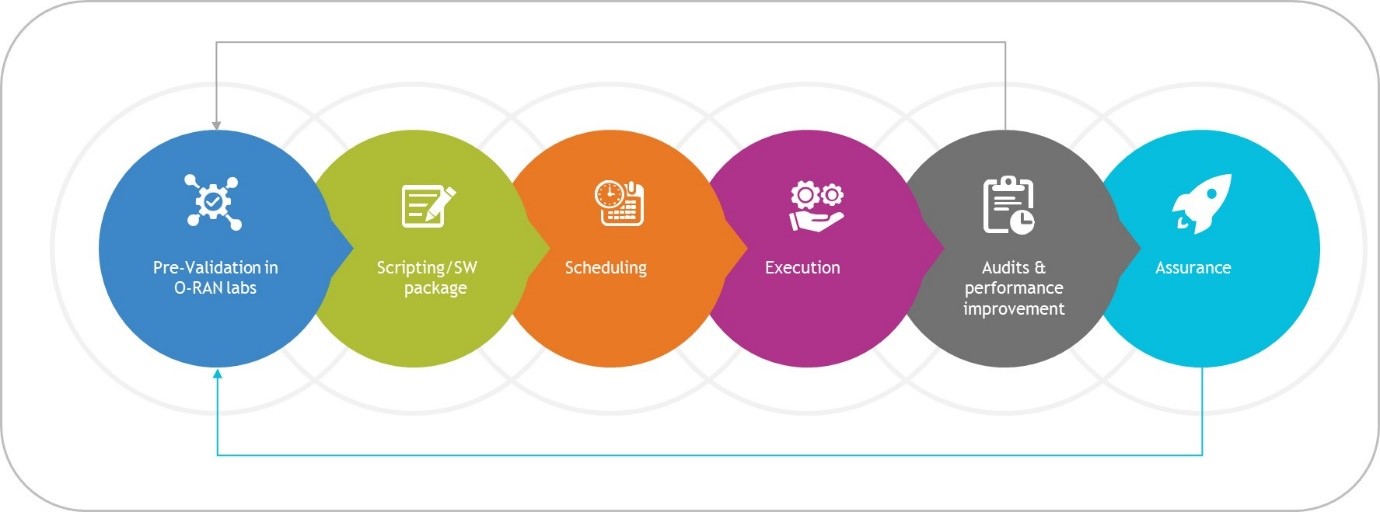
Figure 2 – O-RAN integration approach
However, the integration process combines components from multiple vendors, which can be lengthy and technology intensive. CSPs need rigorous lab testing during the pre- and post-integration stages to ensure successful O-RAN implementation.
System integrators with deep telecom knowledge and O-RAN system integration expertise (RAN architecture, RIC orchestration, deployment and assurance) can make deployment faster.
Integrating Open RAN into existing network infrastructure can be simplified and streamlined by leveraging the power of DevOps tools and practices. Container orchestration platforms, Kubernetes and OpenShift, effectively manage and scale Open RAN components. Embracing modern tools also makes the integration process more efficient and error-free.
Popular tools to manage O-RAN
| Version control | The O-RAN software community provides release packages and interfaces for lab and simulator environments. Git, a version control system, facilitates seamless code tracking and collaboration. |
| Configuration management | Ansible automates repetitive tasks and ensures consistent deployment configurations. |
| Project management | Jira, a popular project management tool, helps teams to organize and track integration efforts. |
| Package manager | Helm charts, a packaging format for Kubernetes apps, simplify the deployment and management of O-RAN components. |
| Data visualization | Grafana provides real-time insights into network performance and health. |
| Monitoring | Prometheus collects and stores metrics for in-depth analysis. |
By adopting these tools and practices, network operators can expect more (10x to 15x) releases – new software features and hardware support – in Open-source technology against conventional RAN OEMs for a robust O-RAN integration.
In summary
O-RAN is more flexible and innovative but still in the early stages of supply chain ecosystem maturity. It is more suitable for greenfield deployments where operators start from scratch. However, for operators with existing networks, ORAN is still in the early stages of development. Brownfield deployments need rigorous lab testing before deployment. Traditional RAN, on the other hand, is more compatible where operators need to upgrade existing networks.
To help CSPs catch the next wave of innovation, TCTS partners with leading O-RAN players to develop strategic and long-term partnerships. This collaboration focuses on comprehensive testing, automation, validation, knowledge sharing, and support transfer. These initiatives enable TCTS to drive innovation and accelerate the adoption of Open RAN technologies, creating a more interconnected and efficient telecommunications ecosystem.
References
[1] RAN accounts for nearly 60-65 percent of the total cost of network ownership [2] A report by Analysysmason





















![Telco Cloud: A Key Enabler to Telco Transformation [Part 1]](https://www.tatacommunications-ts.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Telco-Cloud-blog_image-1-500x383.png)








